CUPCAKE
STIMULI
Add vignette condition. Is the neural basis for the coarse-scale orientation bias a by-product of stimulus properties, like edge or vignette?
Roth 2018
Broderick Winawer 2018
sketch 290519
sketch 230519
check rd_grating function
check ims with cosyne aperture from rd_cupcakeAperture
check ims with cosyne-ring aperture
check ims with radial-sine-ring aperture



Logo Modernism (Müller, Widermann 2019) p.217
Logo Modernism (Müller, Widermann 2019)
grating
+
aperture
=
stimulus
isolate every other ring from aperture
make hard edge
1-grating for isolated positions
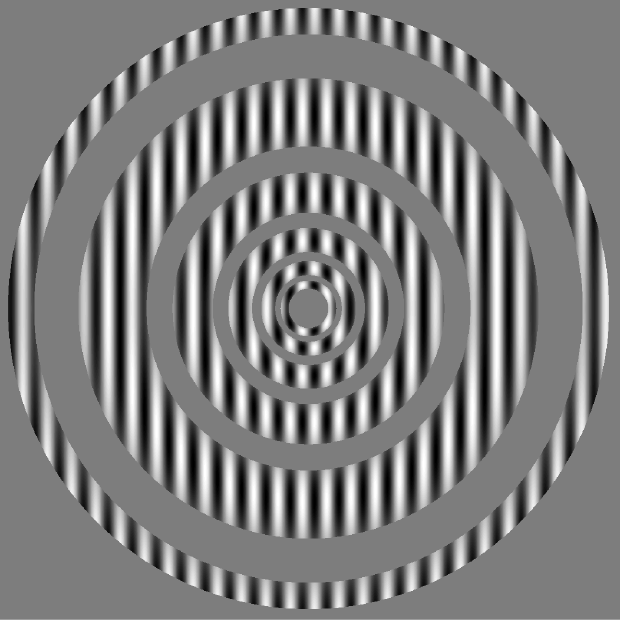
radial eccentricity scaled vignette
vignette with hard edge
vignette hooray (added as 'vignette' case to rd_aperture in google drive)
unsuccessful earlier attempt
repositories for generating stimuli
Stimulus vignetting and orientation selectivity in human visual cortex![]() (Merriam, Roth 2018)
(Merriam, Roth 2018)
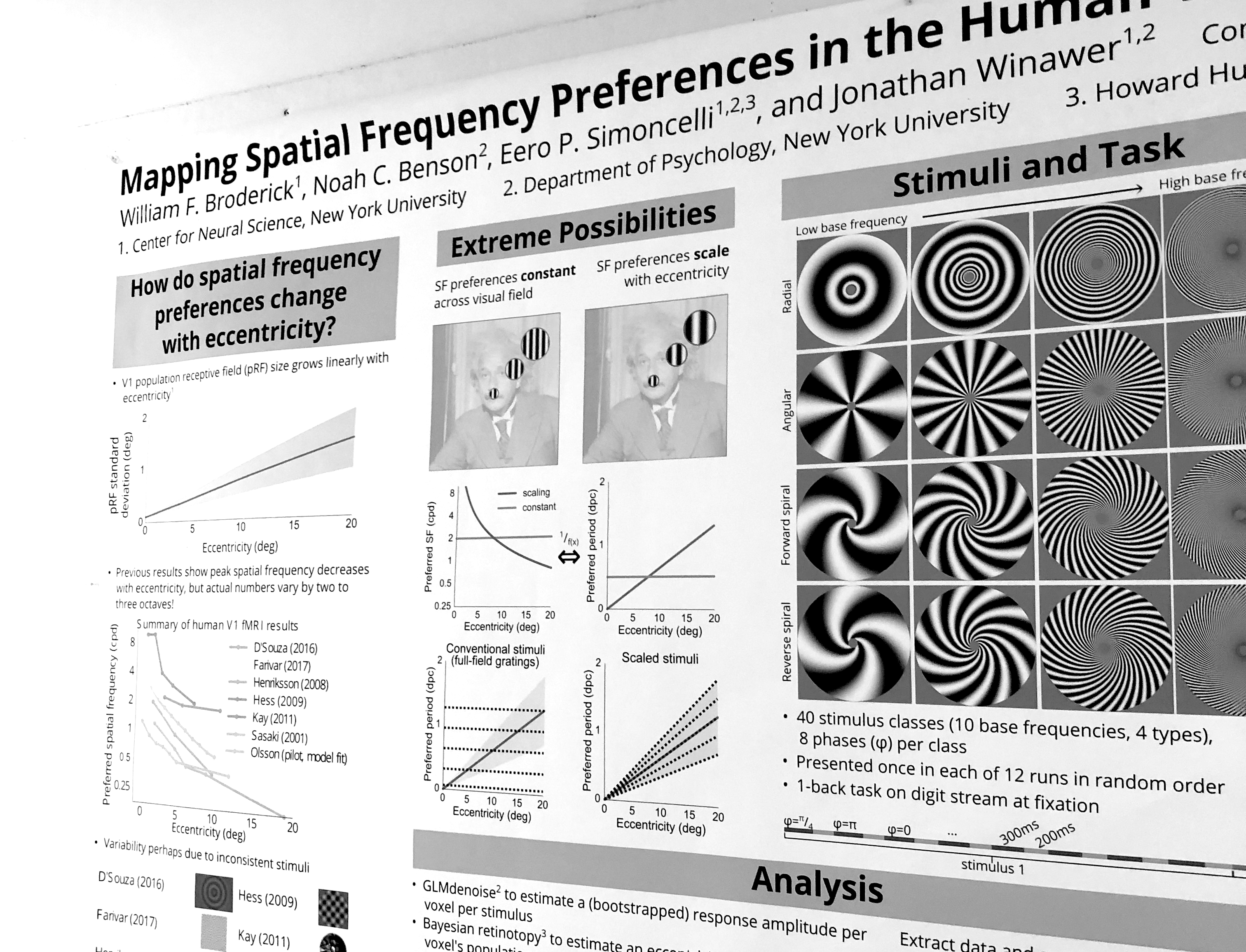
Mapping spatial frequency preferences in the human visual cortex (Broderick, Winawer 2018)
PUPIL

kt_eyeExport.m
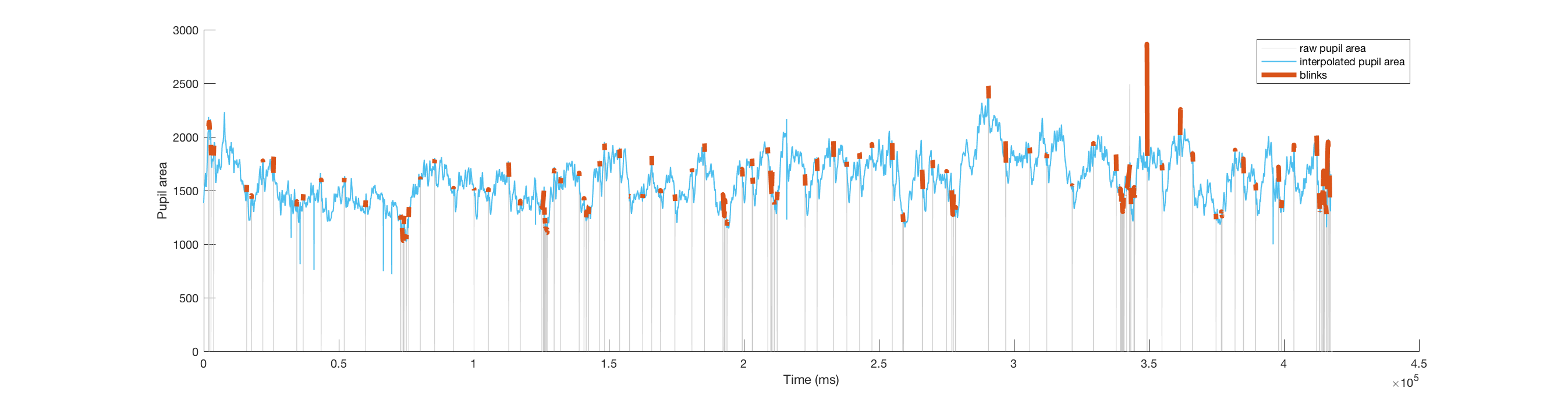
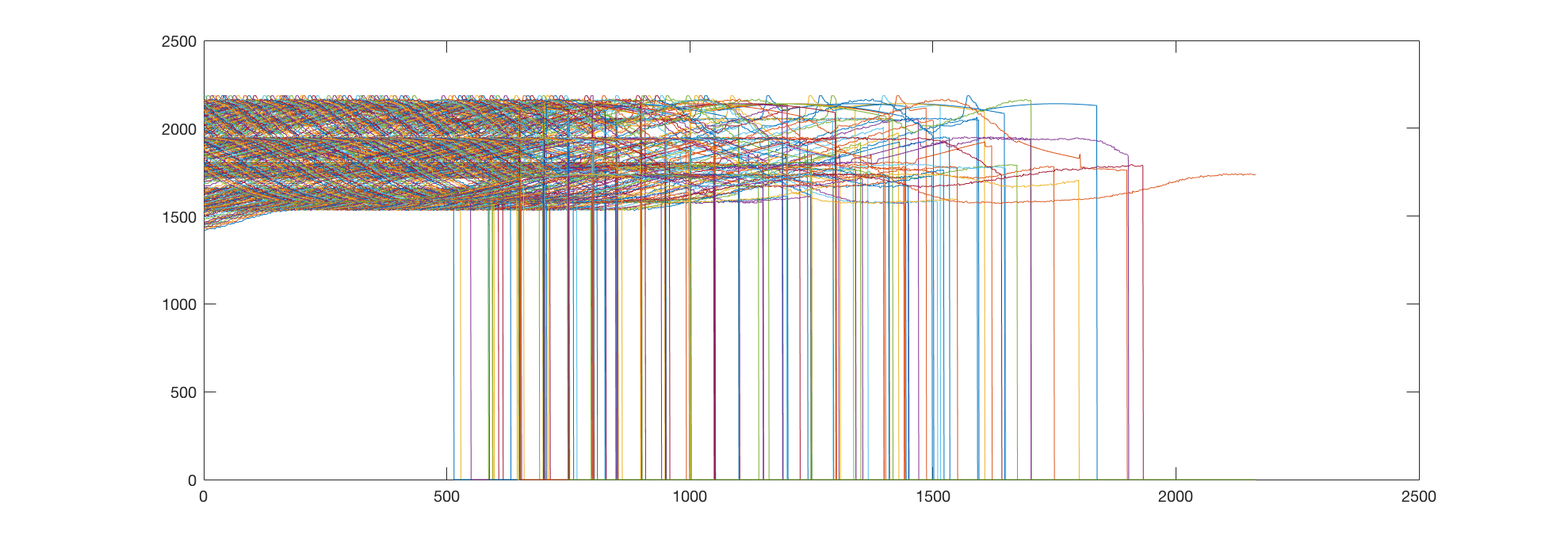
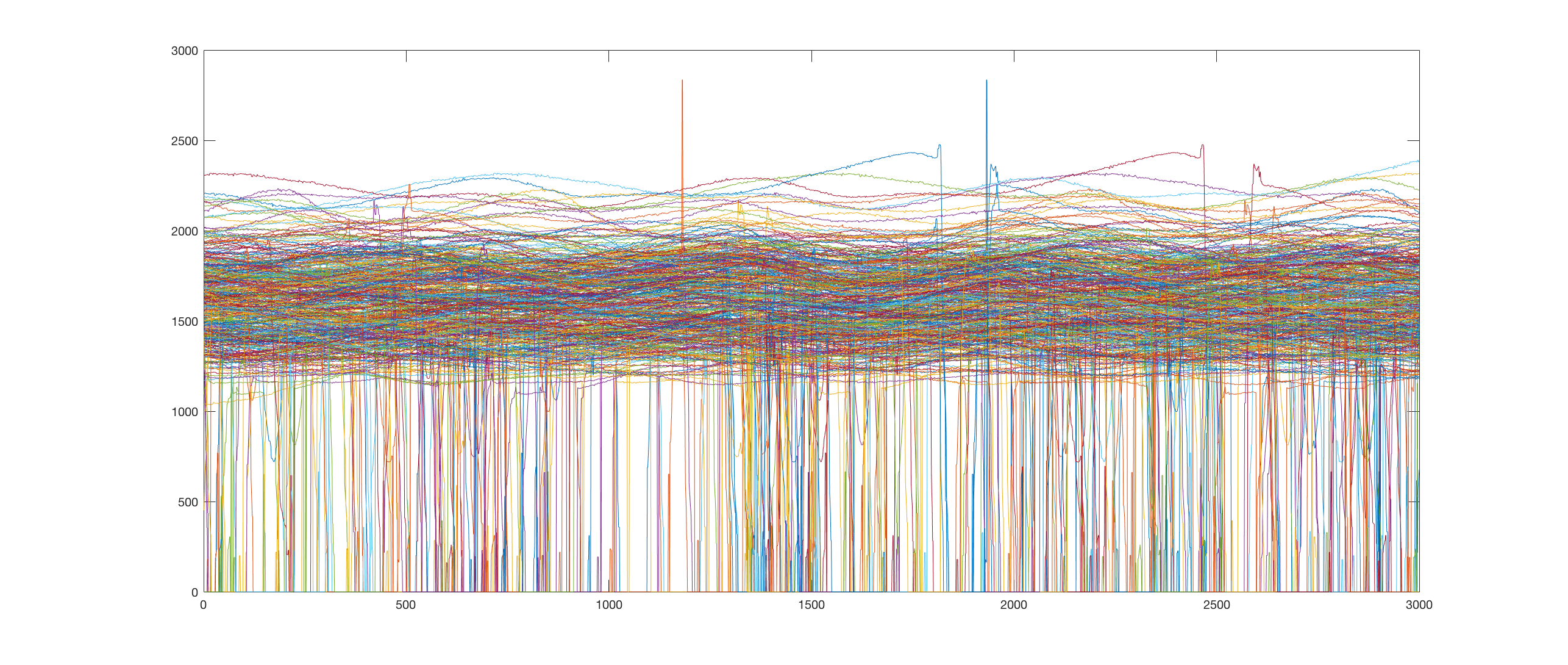

loop threshhold -0.35

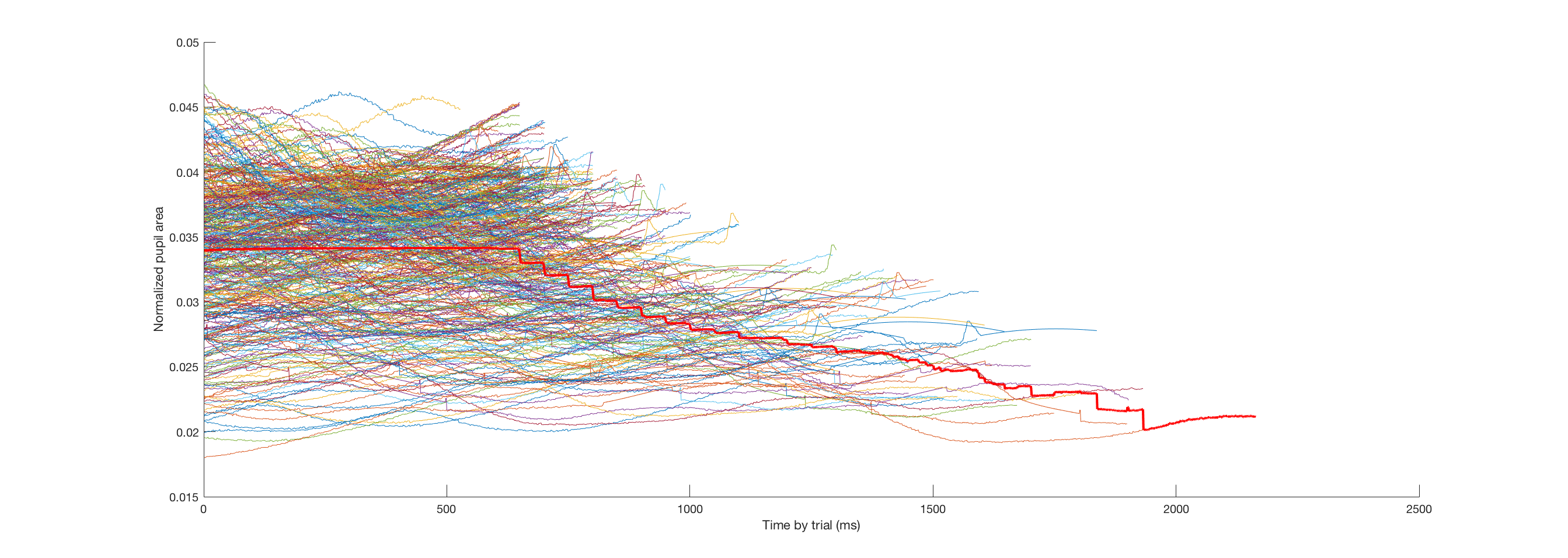
pupil area (1st half trials, 2nd half)

MEG
FFT = fast fourier transform, transforms signal from time to frequency domain
rd_Cupcake2.m
rd_Cupcake2.m, plot all trials for several channels, one orientation

rd_cupcake2, topo movie
0ms
60ms
120ms
150ms
READINGS
1. How is orientation processed?
- Wandell chapter
- check Kandel book
2. Objective vs. subjective perception, confidence
- Review on confidence: Mamassian 2016
- Refs 7, 9, 10 from the grant proposal
- Peters et al. 2017
- Rausch et al. 2018
3. MEG background
- Primer on how MEG contributes to neuroscience
- A more technical intro
4. Inverted encoding models (IEMs) to reconstruct orientation
- Brouwer & Heeger 2009
- Garcia et al. 2013
- King et al. 2016
5. What can we learn from IEMs and other population measures of orientation selectivity?
- Liu et al. 2018
- Sprague et al. 2018
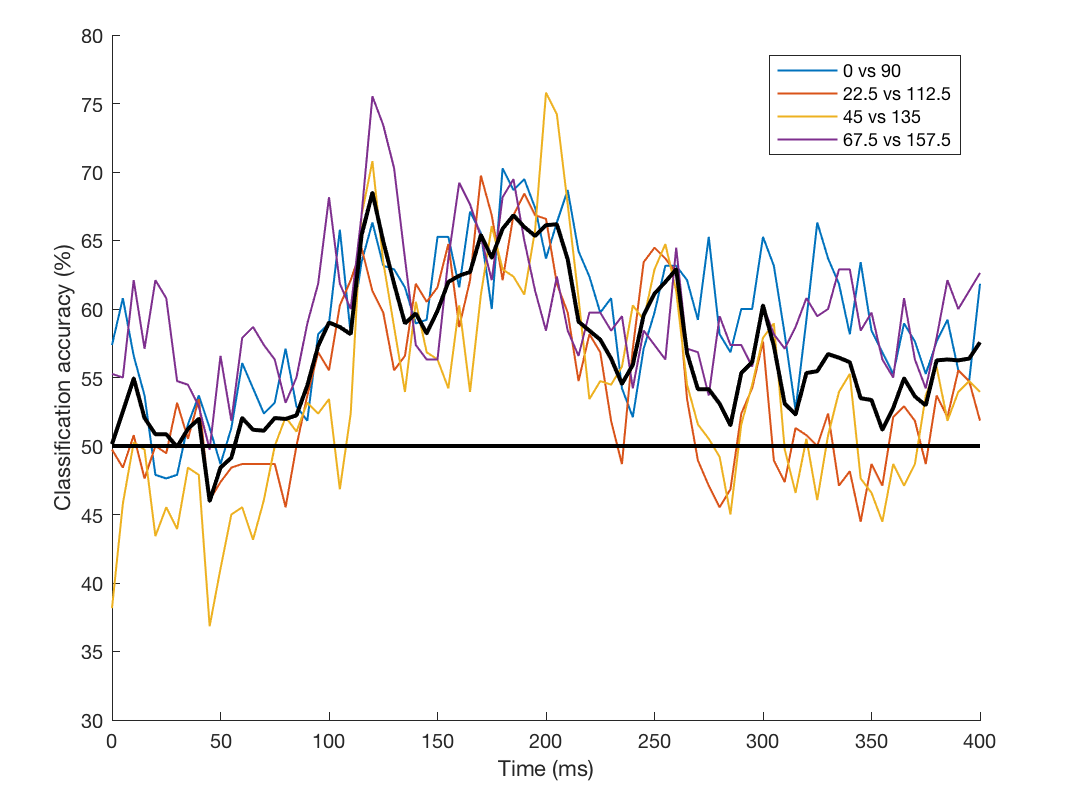
- Roth et al. 2018![]()
CUPCAKE
STIMULI
Add vignette condition. Is the neural basis for the coarse-scale orientation bias a by-product of stimulus properties, like edge or vignette?

Roth 2018
Broderick Winawer 2018
check rd_grating function
check ims with cosyne aperture from rd_cupcakeAperture
check ims with cosyne-ring aperture
check ims with radial-sine-ring aperture
grating
+
aperture
=
stimulus
isolate every other ring from aperture
make hard edge
1-grating for isolated positions

radial eccentricity scaled vignette
vignette with hard edge
vignette hooray (added as 'vignette' case to rd_aperture in google drive)
unsuccessful earlier attempt
PUPIL

kt_eyeExport.m





loop threshhold -0.35

pupil area (1st half trials, 2nd half)

MEG
FFT = fast fourier transform, transforms signal from time to frequency domain
rd_Cupcake2.m
rd_Cupcake2.m, plot all trials for several channels, one orientation

rd_cupcake2, topo movie
0ms
60ms
120ms
150ms

READINGS
1. How is orientation processed?
- Wandell chapter
- check Kandel book
2. Objective vs. subjective perception, confidence
- Review on confidence: Mamassian 2016
- Refs 7, 9, 10 from the grant proposal
- Peters et al. 2017
- Rausch et al. 2018
3. MEG background
- Primer on how MEG contributes to neuroscience
- A more technical intro
4. Inverted encoding models (IEMs) to reconstruct orientation
- Brouwer & Heeger 2009
- Garcia et al. 2013
- King et al. 2016
5. What can we learn from IEMs and other population measures of orientation selectivity?
- Liu et al. 2018
- Sprague et al. 2018
- Roth et al. 2018![]()